Hirsutism/Abnormal Hair Growth
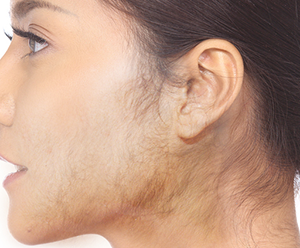
What is Hirsutism?
Hirsutism is a condition characterized by the excessive growth of body or facial hair in women, much like hair growth patterns seen in men. The hair grows thick and dark on the face (resembling a moustache and beard), chest, back, upper arms, lower stomach, around the nipples and legs. Hirsutism may be related to menstrual disorders.
Causes of Hirsutism
Hormones play an important role in regulating growth and other bodily functions. At the onset of puberty, a mixture of female and male sex hormones is produced for sexual maturity. An imbalance in these hormones or increased production of male hormones can lead to hirsutism (high levels of the male sex hormone androgen). The recent increase in childhood and adolescent obesity is also a major factor that has led to a high incidence of hirsutism.
Causes of Hirsutism
- Polycystic ovary syndrome
- Cushing’s syndrome (high levels of cortisol, a steroid hormone)
- Congenital adrenal hyperplasia (an inherited condition characterized by abnormal levels of cortisol and androgen)
- A tumour (tumour in adrenal gland or ovaries)
- Certain medications
Symptoms of Menstrual Disorders and Hirsutism
The symptoms of hirsutism include:
- Acne
- Balding
- Deepening voice
- Reduced breast size
- Enlargement of clitoris
Diagnosis of Hirsutism
Your doctor will collect your medical history to understand the reason behind your condition. You may be ordered blood tests to evaluate the variation in the levels of the hormone. A high level of the male hormone testosterone in the blood confirms hirsutism. An ultrasound examination or CT scan may be ordered to examine the presence of cysts, fibroids or tumours in your ovaries. Laparoscopic examination and biopsy may be performed to diagnose cancer.
Treatment for Hirsutism
Your doctor may prescribe hormone therapy or oral contraceptive pills to treat hirsutism. Other cosmetic procedures, such as electrolysis (mild current targeted at hair follicles) and laser therapy (laser beam targeted over the skin to destroy hair follicles), and temporary hair removal procedures (waxing, shaving, etc.) may help to control the excessive growth of hair.







